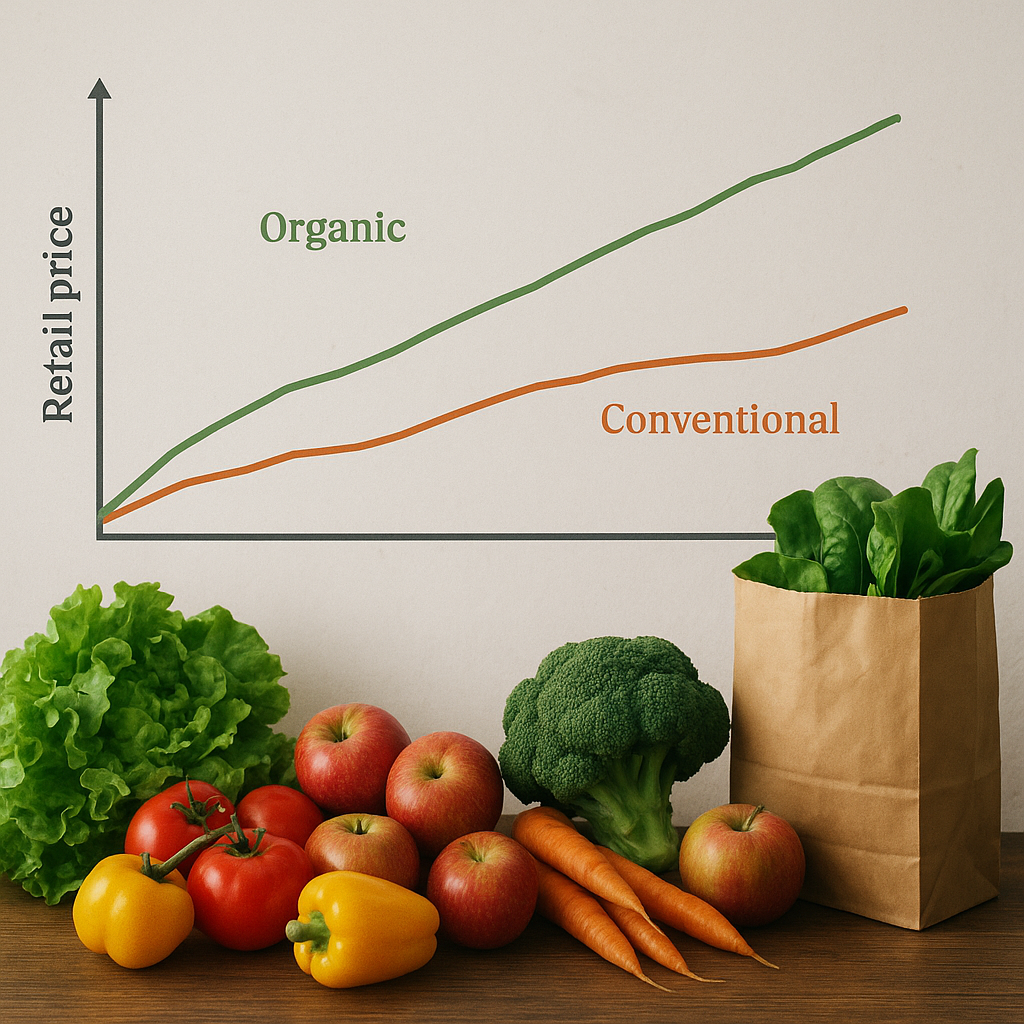
Agriculture and agricultural price analysis are critical components of the global economy, influencing food security, trade policies, and economic stability. This article delves into the intricacies of agricultural practices and the complex dynamics of agricultural price analysis, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential topics.
Chapter 1: The Fundamentals of Agriculture
Introduction to Agriculture
Agriculture is the practice of cultivating soil, growing crops, and raising animals for food, fiber, medicinal plants, and other products used to sustain and enhance human life. It is one of the oldest and most vital human activities, forming the backbone of civilizations and economies throughout history. The development of agriculture allowed human societies to transition from nomadic lifestyles to settled communities, leading to the rise of cities and complex societies.
Types of Agriculture
Agriculture can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its unique characteristics and methods:
- Subsistence Agriculture: This type of agriculture is practiced primarily for self-consumption, with little surplus for trade. It is common in developing countries and involves small-scale farming with traditional methods.
- Commercial Agriculture: In contrast to subsistence agriculture, commercial agriculture focuses on producing crops and livestock for sale in the market. It involves large-scale farming, advanced technology, and significant capital investment.
- Industrial Agriculture: This form of agriculture is characterized by the use of modern machinery, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to maximize production efficiency and output.
- Organic Agriculture: Organic farming emphasizes sustainable practices, avoiding synthetic chemicals and GMOs. It focuses on maintaining soil health, biodiversity, and ecological balance.
Key Agricultural Practices
Several essential practices are fundamental to successful agriculture:
- Crop Rotation: The practice of growing different types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons to improve soil health and reduce pest and disease problems.
- Soil Management: Techniques such as tilling, fertilization, and irrigation are used to maintain soil fertility and structure, ensuring optimal growing conditions for crops.
- Pest and Disease Control: Integrated pest management (IPM) and other strategies are employed to protect crops from pests and diseases while minimizing environmental impact.
- Water Management: Efficient irrigation systems and water conservation practices are crucial for sustaining agriculture, especially in regions with limited water resources.
Chapter 2: Agricultural Price Analysis
Understanding Agricultural Prices
Agricultural price analysis involves examining the factors that influence the prices of agricultural commodities, such as crops and livestock. Prices are determined by the interplay of supply and demand, production costs, market conditions, and external factors like weather, trade policies, and global economic trends.
Factors Influencing Agricultural Prices
Several key factors impact agricultural prices:
- Supply and Demand: The fundamental economic principle of supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining agricultural prices. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall, and when demand outstrips supply, prices rise.
- Production Costs: The costs associated with producing agricultural commodities, including inputs like seeds, fertilizers, labor, and machinery, directly affect prices. Higher production costs can lead to higher prices for consumers.
- Weather and Climate: Weather conditions and climate patterns significantly impact agricultural production. Droughts, floods, and other extreme weather events can reduce crop yields and drive up prices.
- Trade Policies: Government policies, tariffs, and trade agreements influence the flow of agricultural goods between countries, affecting prices on both domestic and international markets.
- Global Economic Trends: Economic conditions, currency exchange rates, and global market trends also play a role in shaping agricultural prices. For example, a strong global economy can boost demand for agricultural products, leading to higher prices.
Methods of Agricultural Price Analysis
Several methods are used to analyze agricultural prices, each offering unique insights into market dynamics:
- Time Series Analysis: This method involves examining historical price data over time to identify trends, patterns, and seasonal variations. Time series analysis can help forecast future price movements based on past behavior.
- Econometric Models: Econometric models use statistical techniques to analyze the relationships between agricultural prices and various influencing factors. These models can provide a deeper understanding of the underlying drivers of price changes.
- Market Surveys: Surveys of farmers, traders, and consumers can provide valuable information about market conditions, production expectations, and price trends. These surveys help capture real-time data and market sentiment.
- Supply and Demand Analysis: This approach involves assessing the balance between supply and demand for specific agricultural commodities. By analyzing production levels, consumption patterns, and inventory levels, analysts can predict price movements.
Challenges in Agricultural Price Analysis
Despite the importance of agricultural price analysis, several challenges complicate the process:
- Data Availability: Access to accurate and timely data is essential for effective price analysis. However, data collection can be challenging, especially in developing regions with limited infrastructure.
- Market Volatility: Agricultural markets are often subject to high volatility due to factors like weather events, geopolitical tensions, and sudden changes in demand. This volatility makes price prediction difficult.
- Complex Interactions: The interactions between various factors influencing agricultural prices are complex and multifaceted. Isolating the impact of individual factors can be challenging.
- Policy Uncertainty: Government policies and regulations can change rapidly, affecting agricultural markets. Analysts must account for potential policy shifts and their implications for prices.
Case Study: Global Maize Prices
To illustrate the principles of agricultural price analysis, let’s examine the case of global maize prices. Maize, also known as corn, is a staple crop with significant economic importance. It is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes, making it a critical commodity in global markets.
Regional Comparison of Maize Prices
Maize prices vary significantly across different regions due to factors such as production levels, consumption patterns, and trade dynamics. Here, we compare maize prices in three key regions: North America, South America, and Sub-Saharan Africa.
North America
North America, particularly the United States, is one of the largest producers and exporters of maize. The region benefits from advanced agricultural technology, extensive infrastructure, and favorable climatic conditions. As a result, maize production is highly efficient, leading to relatively stable prices. However, factors such as trade policies, biofuel demand, and weather events can still influence prices.
South America
South America, especially Brazil and Argentina, is another major player in the global maize market. The region has seen significant growth in maize production due to expanding agricultural land and improved farming practices. However, South American maize prices can be more volatile due to factors like currency fluctuations, transportation challenges, and political instability.
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa faces unique challenges in maize production and pricing. The region relies heavily on maize as a staple food, but production is often hindered by limited access to technology, poor infrastructure, and adverse weather conditions. As a result, maize prices in Sub-Saharan Africa can be highly volatile, with significant implications for food security and economic stability.
Conclusion
Agriculture and agricultural price analysis are essential for understanding the dynamics of global food systems and ensuring economic stability. By examining the factors influencing agricultural prices and employing various analytical methods, stakeholders can make informed decisions to navigate the complexities of agricultural markets. The case study of global maize prices highlights the importance of regional comparisons in understanding the diverse factors that shape agricultural prices worldwide.