Introduction
Agriculture has always been a cornerstone of human civilization, providing the essential resources needed for survival and economic development. In recent years, the agricultural sector has seen significant changes, particularly in the realm of organic farming. This article delves into the intricate world of agriculture and agricultural price analysis, with a specific focus on comparing the prices of organic and conventional spices on a global scale. By examining various factors that influence these prices, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics at play in this crucial sector.
Chapter 1: The Agricultural Landscape
The Evolution of Agriculture
Agriculture has undergone a remarkable transformation over the centuries. From the early days of subsistence farming to the modern era of industrial agriculture, the methods and technologies employed have evolved significantly. The Green Revolution of the mid-20th century marked a turning point, introducing high-yield crop varieties, chemical fertilizers, and advanced irrigation techniques. These innovations led to a substantial increase in agricultural productivity, helping to feed a growing global population.
Organic Farming: A Rising Trend
In recent decades, there has been a growing interest in organic farming as an alternative to conventional agricultural practices. Organic farming emphasizes the use of natural inputs, such as compost and biological pest control, while avoiding synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This approach is not only seen as more environmentally sustainable but also as a way to produce healthier and safer food products.
Conventional Farming: The Dominant Force
Despite the rise of organic farming, conventional agriculture remains the dominant force in the global food system. Conventional farming relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides to maximize crop yields. While this approach has been highly effective in meeting the food demands of a growing population, it has also raised concerns about environmental degradation, soil health, and the long-term sustainability of agricultural practices.
Chapter 2: Agricultural Price Analysis
Factors Influencing Agricultural Prices
The prices of agricultural products are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including supply and demand dynamics, weather conditions, input costs, and government policies. Understanding these factors is crucial for analyzing price trends and making informed decisions in the agricultural sector.
- Supply and Demand: The basic economic principle of supply and demand plays a significant role in determining agricultural prices. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall, and vice versa. Factors such as crop yields, harvest seasons, and global trade can all impact supply and demand dynamics.
- Weather Conditions: Weather is a critical factor in agriculture, as it directly affects crop growth and yields. Droughts, floods, and other extreme weather events can disrupt production and lead to price volatility.
- Input Costs: The cost of inputs, such as seeds, fertilizers, and labor, can significantly impact agricultural prices. Rising input costs can lead to higher production costs, which may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Government Policies: Agricultural policies, including subsidies, tariffs, and trade agreements, can influence prices by affecting production levels and market access. For example, subsidies for certain crops can lead to overproduction and lower prices, while trade restrictions can limit market access and drive up prices.
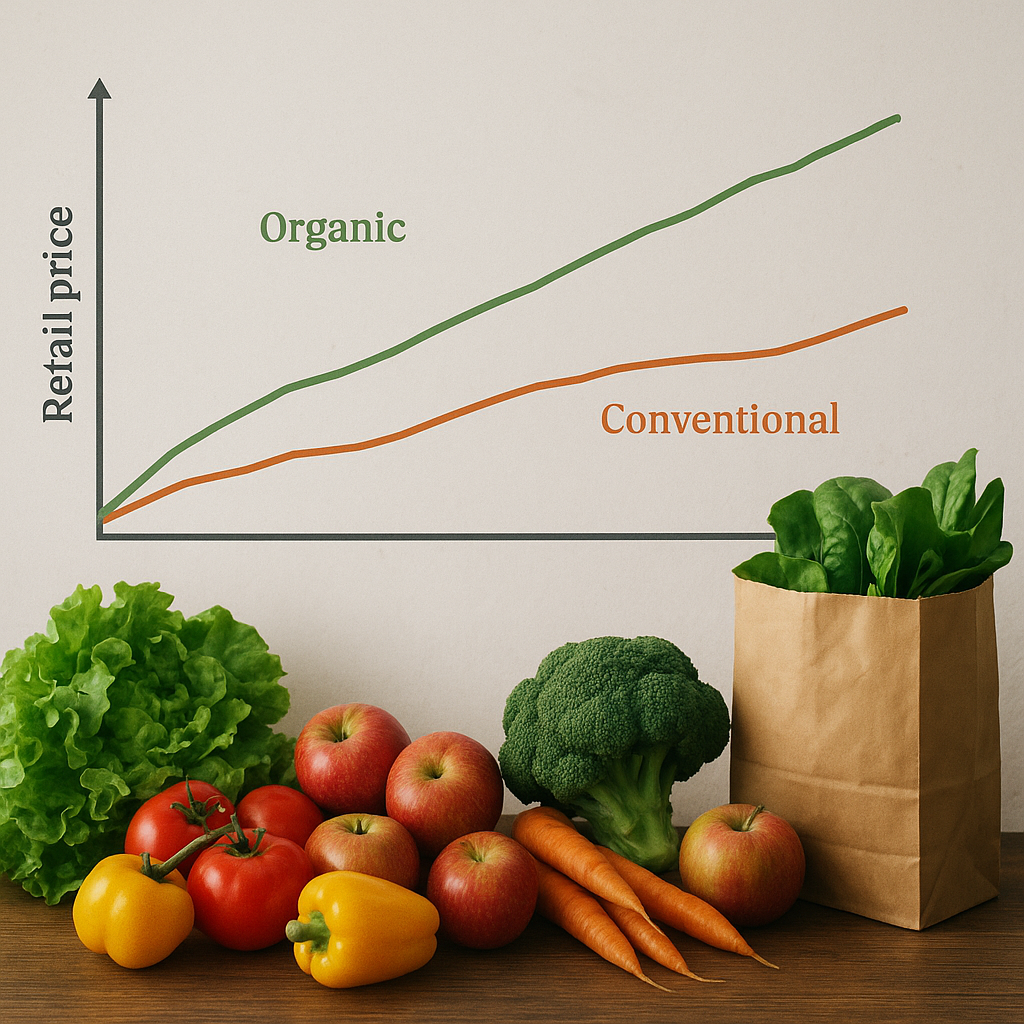
Price Analysis of Organic vs. Conventional Spices
When it comes to spices, the price difference between organic and conventional products is often a topic of interest for both consumers and producers. Organic spices are typically more expensive than their conventional counterparts, and several factors contribute to this price disparity.
- Production Costs: Organic farming practices generally involve higher production costs due to the use of natural inputs and labor-intensive methods. For example, organic farmers may rely on manual weeding instead of chemical herbicides, which can increase labor costs.
- Certification and Compliance: Obtaining organic certification involves rigorous standards and regular inspections, which can be costly for farmers. These costs are often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for organic products.
- Market Demand: There is a growing demand for organic products, driven by consumer preferences for healthier and more environmentally friendly options. This increased demand can lead to higher prices for organic spices.
- Supply Chain Factors: The supply chain for organic products is often less developed than that for conventional products, leading to higher transportation and distribution costs. Additionally, organic products may require separate processing and storage facilities to prevent contamination with conventional products.
Global Price Comparison
The prices of organic and conventional spices can vary significantly across different regions and markets. Several factors contribute to these regional price differences, including local production conditions, market demand, and trade policies.
- Regional Production Conditions: The availability of suitable land, climate, and resources for spice cultivation can impact production costs and prices. For example, regions with favorable growing conditions for organic spices may have lower production costs and, consequently, lower prices.
- Market Demand: Consumer preferences for organic products can vary by region, influencing the demand and prices for organic spices. In regions with high demand for organic products, prices may be higher due to increased competition for limited supplies.
- Trade Policies: Import and export regulations, tariffs, and trade agreements can affect the prices of spices in different markets. For example, regions with restrictive trade policies may have higher prices for imported organic spices due to limited market access.
Chapter 3: Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Case Study: Organic Spice Production in India
India is one of the largest producers and exporters of spices in the world, with a rich history of spice cultivation. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in organic spice production in India, driven by both domestic and international demand.
Organic spice farming in India faces several challenges, including the high cost of organic inputs, limited access to organic certification, and the need for specialized knowledge and training. Despite these challenges, many farmers have successfully transitioned to organic farming and are reaping the benefits of higher prices for their products.
For example, organic turmeric from India is highly sought after in international markets due to its superior quality and health benefits. The price of organic turmeric is often significantly higher than that of conventional turmeric, reflecting the premium that consumers are willing to pay for organic products.
Case Study: Conventional Spice Production in Vietnam
Vietnam is another major player in the global spice market, known for its production of black pepper, cinnamon, and other spices. Conventional spice farming in Vietnam is characterized by the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides to maximize yields and reduce production costs.
While conventional spice farming has been highly successful in terms of production volume and export earnings, it has also raised concerns about environmental sustainability and the long-term health of agricultural ecosystems. The use of chemical inputs can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and other negative environmental impacts.
Despite these challenges, conventional spices from Vietnam remain competitive in global markets due to their lower prices compared to organic alternatives. For example, the price of conventional black pepper from Vietnam is often lower than that of organic black pepper from other regions, making it an attractive option for price-sensitive consumers.
Chapter 4: Future Trends and Implications
The Growing Demand for Organic Products
The demand for organic products, including spices, is expected to continue growing in the coming years. This trend is driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and environmental issues, as well as a growing preference for natural and sustainably produced foods.
As demand for organic spices increases, prices are likely to remain higher than those of conventional spices. However, the price gap may narrow over time as more farmers adopt organic practices and the supply of organic spices increases. Additionally, advancements in organic farming techniques and technologies could help reduce production costs and make organic spices more affordable for consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities for Farmers
Farmers face both challenges and opportunities in the evolving agricultural landscape. For conventional farmers, the challenge lies in balancing the need for high yields and low production costs with the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. For organic farmers, the challenge is to overcome the higher production costs and certification requirements while meeting the growing demand for organic products.
Despite these challenges, there are significant opportunities for farmers who can successfully navigate the transition to organic farming. The premium prices for organic spices can provide higher income and better livelihoods for farmers, while also contributing to environmental sustainability and improved soil health.
Policy Implications and Recommendations
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the agricultural sector and influencing the prices of agricultural products. To support the growth of organic farming and ensure the sustainability of conventional farming, policymakers should consider the following recommendations:
- Incentives for Organic Farming: Provide financial incentives, such as subsidies and grants, to encourage farmers to adopt organic practices and obtain organic certification.
- Research and Development: Invest in research and development to improve organic farming techniques and technologies, reduce production costs, and enhance the quality and yield of organic crops.
- Education and Training: Offer education and training programs to help farmers acquire the knowledge and skills needed for successful organic farming.
- Market Access: Facilitate market access for organic products by reducing trade barriers, promoting fair trade practices, and supporting the development of organic supply chains.
- Environmental Regulations: Implement and enforce environmental regulations to minimize the negative impacts of conventional farming practices and promote sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion
The comparison of organic and conventional spice prices provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the agricultural sector and the factors that influence agricultural prices. While organic spices are generally more expensive than conventional spices, the growing demand for organic products and the potential benefits of organic farming make it an attractive option for both consumers and producers.
As the agricultural landscape continues to evolve, it is essential for farmers, policymakers, and consumers to work together to promote sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. By supporting the growth of organic farming and addressing the challenges faced by conventional farmers, we can ensure a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system for future generations.