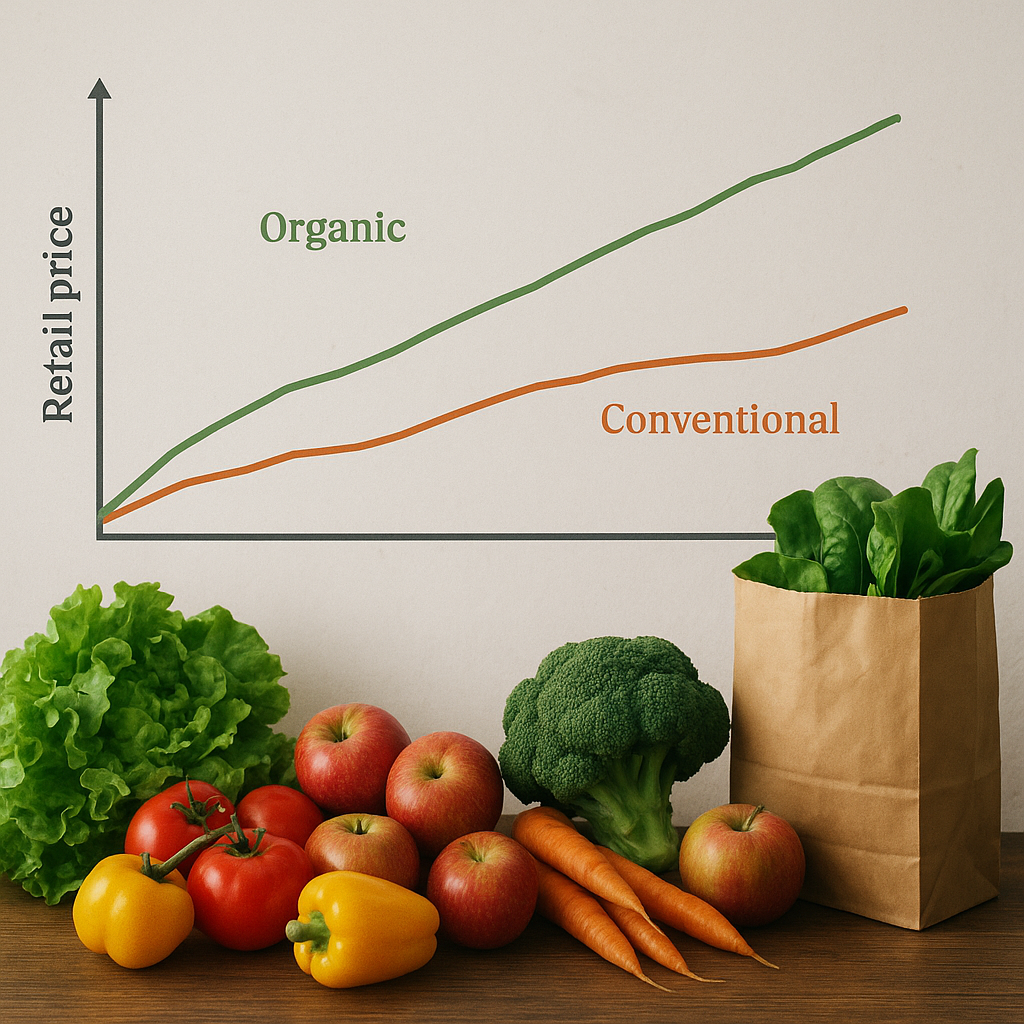
Agriculture and agricultural price analysis are critical components of the global economy, influencing food security, trade balances, and the livelihoods of millions of people. This article delves into the intricate world of agriculture, examining the factors that drive agricultural production and the complex mechanisms behind agricultural price analysis. By understanding these elements, stakeholders can make informed decisions that promote sustainable agricultural practices and economic stability.
The Importance of Agriculture in the Global Economy
Agriculture is the backbone of many economies, particularly in developing countries where it often accounts for a significant portion of GDP and employment. The sector provides essential raw materials for food production, textiles, and biofuels, among other industries. Moreover, agriculture plays a vital role in ensuring food security, which is crucial for the stability and well-being of societies.
Economic Contributions
Agriculture contributes to the economy in several ways. Firstly, it generates income for farmers and agricultural workers, which in turn stimulates local economies. Secondly, agricultural exports can be a significant source of foreign exchange, helping to balance trade deficits. Countries like Brazil, the United States, and China are major exporters of agricultural products, including soybeans, corn, and rice, which are essential commodities in the global market.
Additionally, agriculture supports a wide range of industries, from food processing to retail. The agricultural supply chain includes various stages such as production, processing, distribution, and retail, each adding value and creating jobs. For instance, the dairy industry not only involves milk production but also cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products, each with its own supply chain and economic impact.
Food Security and Sustainability
Food security is a critical issue that agriculture directly addresses. A stable and productive agricultural sector ensures a consistent supply of food, reducing the risk of hunger and malnutrition. However, achieving food security is not just about increasing production; it also involves sustainable practices that protect the environment and ensure long-term productivity.
Sustainable agriculture practices include crop rotation, organic farming, and the use of renewable resources. These methods help maintain soil fertility, reduce the use of harmful chemicals, and promote biodiversity. Governments and international organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable agriculture and are implementing policies and programs to support it.
Factors Influencing Agricultural Production
Agricultural production is influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from climatic conditions to technological advancements. Understanding these factors is essential for effective agricultural planning and policy-making.
Climatic Conditions
Climate is one of the most significant factors affecting agricultural production. Temperature, rainfall, and seasonal variations can all impact crop yields and livestock productivity. For example, droughts can lead to crop failures, while excessive rainfall can cause flooding and soil erosion. Climate change is exacerbating these challenges, making it increasingly important for farmers to adopt resilient agricultural practices.
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is an approach that seeks to increase productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to climate change. CSA practices include the use of drought-resistant crop varieties, efficient irrigation systems, and agroforestry. By adopting these practices, farmers can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change and ensure sustainable production.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have revolutionized agriculture, making it more efficient and productive. Innovations such as precision farming, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and advanced irrigation systems have significantly increased crop yields and reduced resource use.
Precision farming involves the use of GPS, sensors, and data analytics to optimize field-level management. This technology allows farmers to apply inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides more accurately, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. GMOs, on the other hand, have been developed to resist pests, tolerate herbicides, and withstand harsh environmental conditions, further boosting productivity.
Advanced irrigation systems, such as drip and sprinkler irrigation, have also improved water use efficiency. These systems deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. As water scarcity becomes a growing concern, efficient irrigation practices will be crucial for sustainable agriculture.
Economic and Policy Factors
Economic and policy factors also play a significant role in agricultural production. Market prices, input costs, and government policies can all influence farmers’ decisions and overall productivity.
Market prices for agricultural products are determined by supply and demand dynamics. High prices can incentivize farmers to increase production, while low prices may discourage it. Input costs, such as seeds, fertilizers, and labor, also affect profitability and production levels. Rising input costs can squeeze farmers’ margins, making it difficult for them to invest in new technologies and practices.
Government policies, including subsidies, tariffs, and trade agreements, can have a profound impact on agriculture. Subsidies can provide financial support to farmers, helping them manage risks and invest in productivity-enhancing technologies. Tariffs and trade agreements, on the other hand, can affect the competitiveness of agricultural products in the global market. For example, trade barriers can limit market access, while free trade agreements can open up new opportunities for export.
Agricultural Price Analysis
Agricultural price analysis involves examining the factors that influence the prices of agricultural products. This analysis is crucial for farmers, policymakers, and market participants to make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The fundamental principle of supply and demand governs agricultural prices. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall, and when demand exceeds supply, prices rise. Several factors can influence supply and demand dynamics in agriculture.
On the supply side, factors such as weather conditions, input costs, and technological advancements can impact production levels. For example, favorable weather conditions can lead to bumper harvests, increasing supply and potentially lowering prices. Conversely, adverse weather conditions can reduce supply and drive prices up.
On the demand side, factors such as population growth, income levels, and consumer preferences can influence the demand for agricultural products. For instance, rising incomes in developing countries can lead to increased demand for high-value products such as meat and dairy. Changes in consumer preferences, such as the growing demand for organic and sustainably produced food, can also impact demand dynamics.
Market Structure and Competition
The structure of agricultural markets and the level of competition can also influence prices. In highly competitive markets, prices are determined by the interaction of numerous buyers and sellers. In contrast, in markets with limited competition, prices may be influenced by a few dominant players.
Market concentration, where a few large firms control a significant share of the market, can lead to price manipulation and reduced competition. For example, in the seed industry, a few multinational corporations dominate the market, potentially influencing prices and limiting choices for farmers. Similarly, in the meatpacking industry, a small number of firms control a large share of the market, affecting prices and market dynamics.
Government regulations and policies can also impact market structure and competition. Antitrust laws, for example, aim to prevent monopolistic practices and promote competition. Trade policies, such as tariffs and quotas, can also influence market dynamics by affecting the flow of agricultural products across borders.
Global Trade and Exchange Rates
Global trade and exchange rates play a significant role in agricultural price analysis. International trade allows countries to export surplus production and import products that are in short supply. However, trade policies, tariffs, and non-tariff barriers can impact the flow of agricultural products and influence prices.
Exchange rates also affect agricultural prices by influencing the competitiveness of exports and imports. A strong domestic currency can make exports more expensive and less competitive in the global market, potentially reducing demand and lowering prices. Conversely, a weak domestic currency can make exports more competitive, increasing demand and driving prices up.
Trade agreements, such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), can also impact agricultural prices by shaping trade flows and market access. These agreements often include provisions on tariffs, quotas, and subsidies, which can influence the competitiveness of agricultural products and affect prices.
Challenges and Opportunities in Agricultural Price Analysis
Agricultural price analysis is a complex and dynamic field, with several challenges and opportunities. Understanding these challenges and opportunities is crucial for effective decision-making and risk management.
Challenges
One of the primary challenges in agricultural price analysis is the inherent volatility of agricultural markets. Prices can fluctuate significantly due to factors such as weather conditions, pest outbreaks, and geopolitical events. This volatility can make it difficult for farmers and market participants to predict prices and manage risks effectively.
Another challenge is the availability and quality of data. Accurate and timely data is essential for effective price analysis, but in many regions, data collection and reporting systems are inadequate. This can lead to information asymmetry, where some market participants have access to better information than others, potentially leading to market distortions.
Additionally, the complexity of global supply chains and the interconnectedness of markets can make price analysis challenging. For example, a disruption in one part of the world, such as a drought in a major grain-producing region, can have ripple effects across global markets, impacting prices and trade flows.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, there are several opportunities in agricultural price analysis. Advances in technology, such as big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, are transforming the field, providing new tools and insights for market participants.
Big data analytics allows for the analysis of vast amounts of data from various sources, such as weather reports, satellite imagery, and market transactions. This can provide valuable insights into market trends, supply and demand dynamics, and price movements. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can further enhance these analyses by identifying patterns and making predictions based on historical data.
Blockchain technology also holds promise for agricultural price analysis by providing a transparent and secure way to track transactions and verify data. This can reduce information asymmetry and increase trust among market participants, leading to more efficient and fair markets.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental stewardship presents opportunities for agricultural price analysis. As consumers and policymakers increasingly prioritize sustainable practices, there is a growing demand for data and analysis on the environmental impact of agricultural production. This can drive the development of new metrics and tools for assessing and valuing sustainability in agriculture.
Conclusion
Agriculture and agricultural price analysis are critical components of the global economy, influencing food security, trade balances, and the livelihoods of millions of people. Understanding the factors that drive agricultural production and the mechanisms behind agricultural price analysis is essential for effective decision-making and risk management.
While there are several challenges in agricultural price analysis, such as market volatility and data limitations, there are also significant opportunities. Advances in technology, the growing emphasis on sustainability, and the interconnectedness of global markets are transforming the field, providing new tools and insights for market participants.
By leveraging these opportunities and addressing the challenges, stakeholders can promote sustainable agricultural practices, enhance food security, and ensure economic stability. As the world continues to evolve, the importance of agriculture and agricultural price analysis will only grow, making it essential for policymakers, farmers, and market participants to stay informed and adapt to changing conditions.